Hello friends,
In this video, we will revise 15th chapter of Science – Our Environment.
In this video, we will be discussing following topics:
- Ecosystem
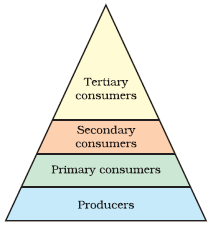
- Producers, consumers and decomposers
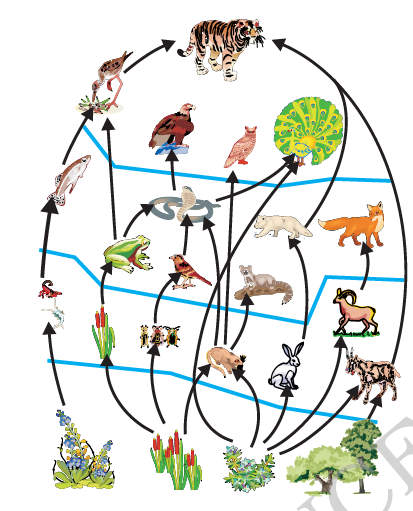
- Food chain
- Food web
- Biological magnification
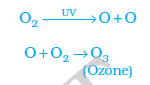
- Ozone layer and its depletion
- Previous Years’ Questions
Let us now start revising this chapter