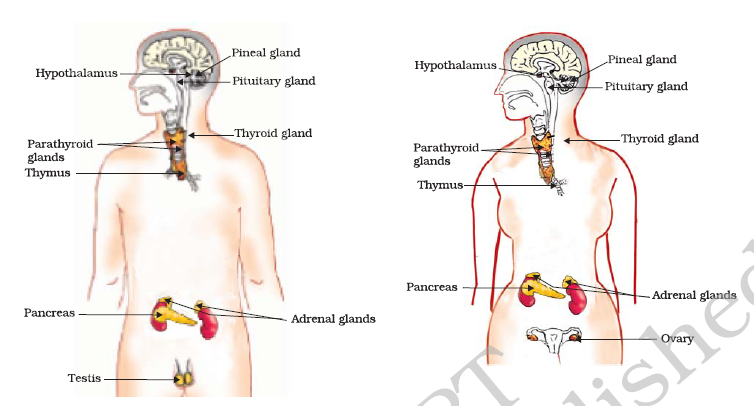
If the amount of any hormone decreases or increases, it can have serious repercussions. For example, if growth hormone is secreted in excess, height of a person increases drastically, leading to a giant. If the amount decreases, it can lead to a condition known as dwarfism, or a person with short height. Thus, the amount of each of these hormones is controlled by some specific feedback mechanisms.
Let us now understand this chapter’s weightage.
In previous years, questions of 1, 2, 3 as well as 5 marks have been asked from this chapter. Thus, to score full marks in this chapter, we suggest that you read this chapter from NCERT thoroughly, as it has some small details which can be asked, like names and functions of hormones, etc.
Also do remember to practice drawing every diagram atleast once, as they have been asked in previous exams.
You can now see all questions appearing in previous years’ papers on your screen now.